Commentary

How has the global market performed?
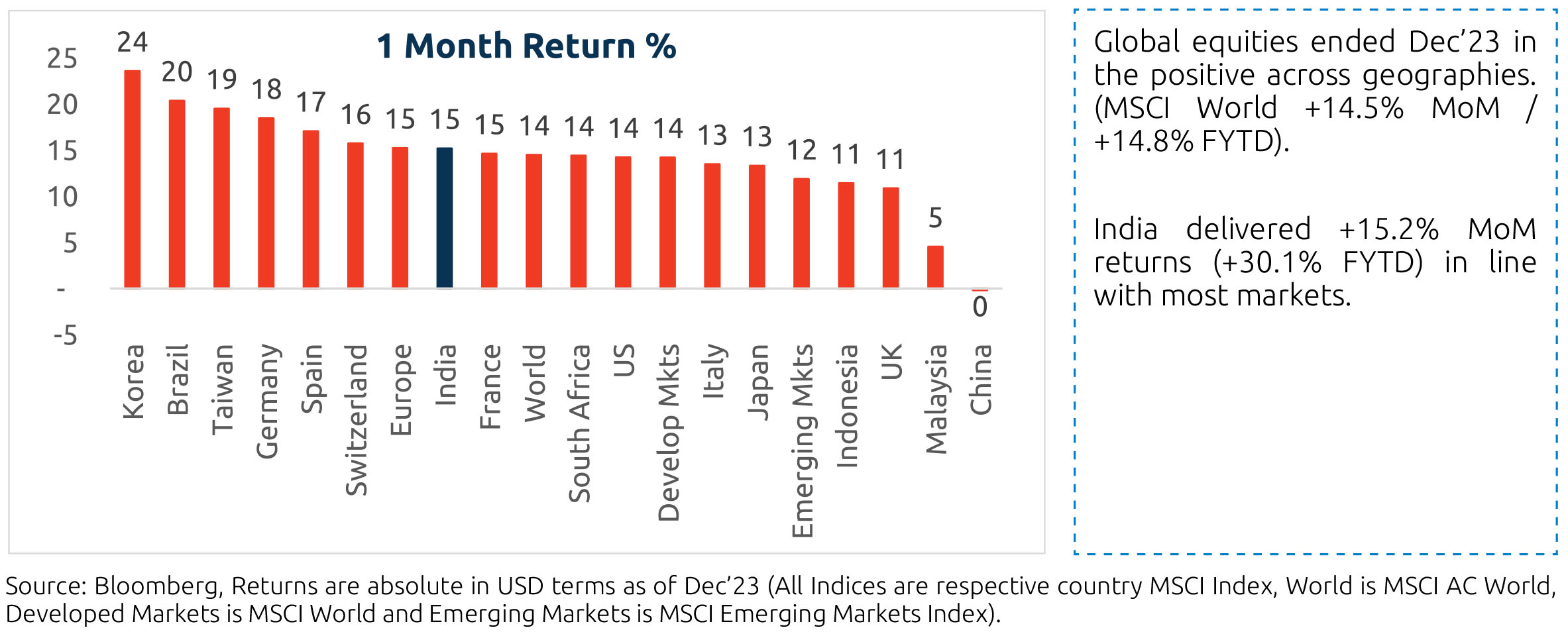
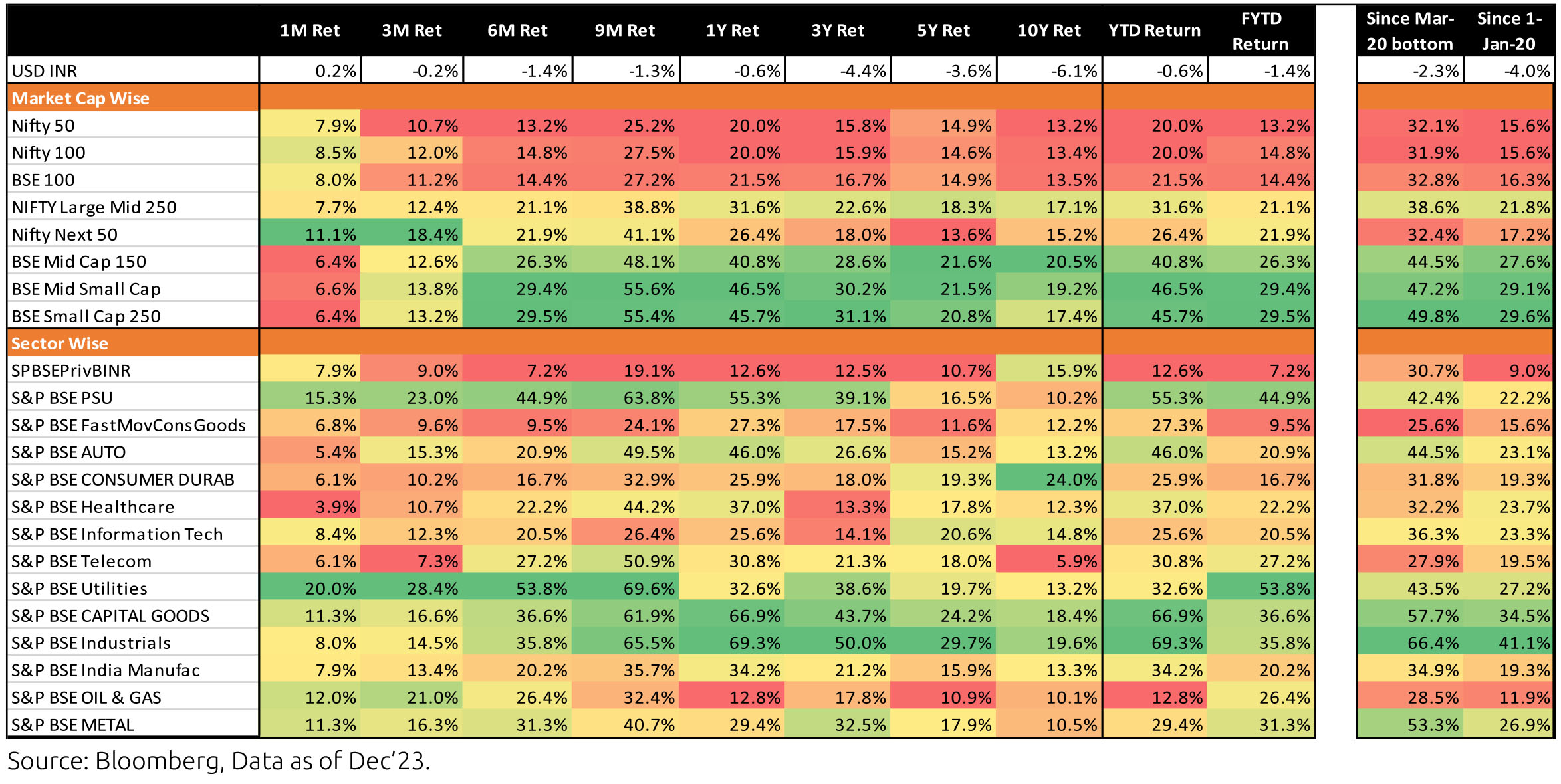
Comparative: India's performance is much better CYTD but leads the pack across all other horizons and geographies
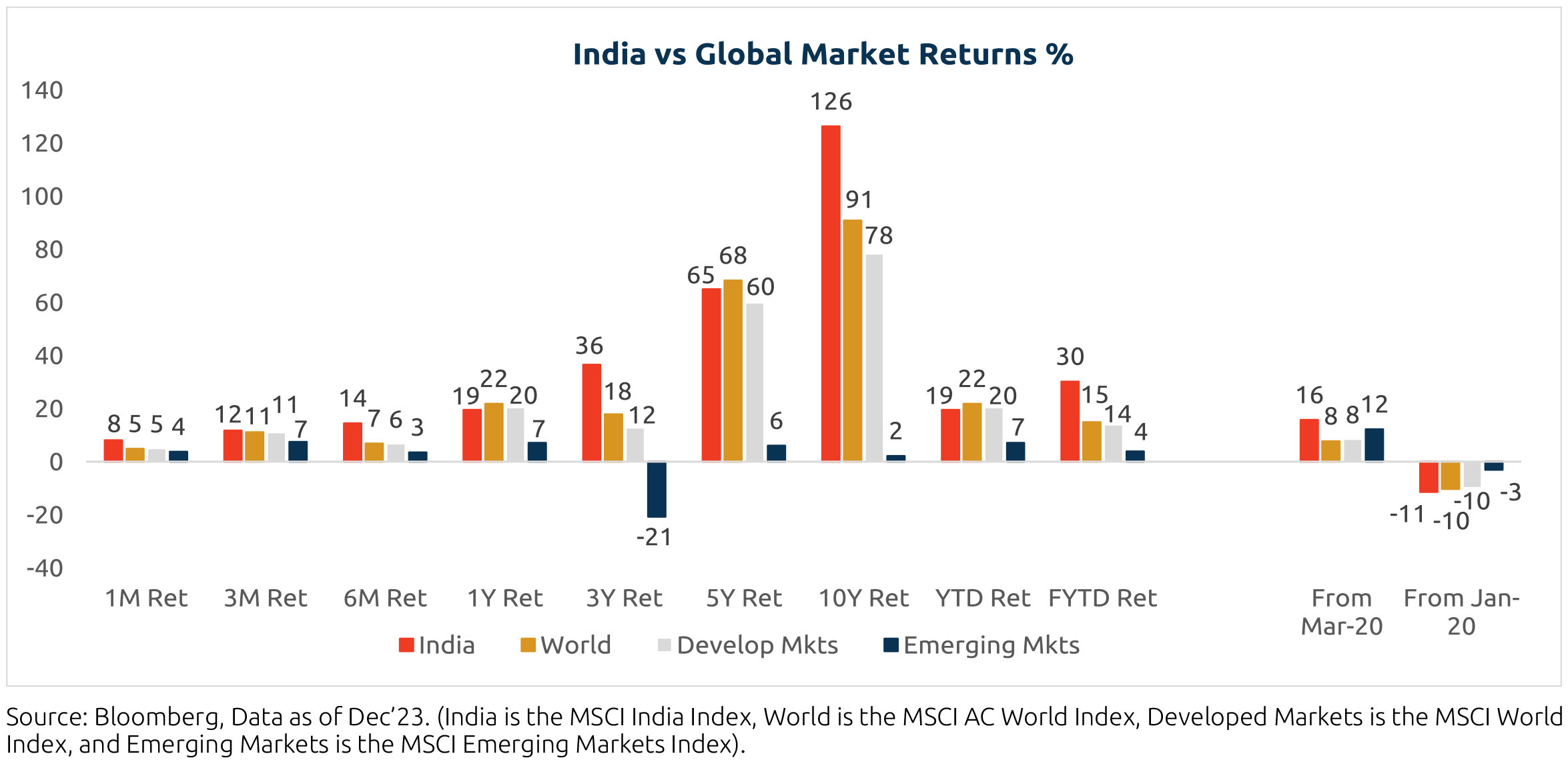
How has the Indian Market performed?
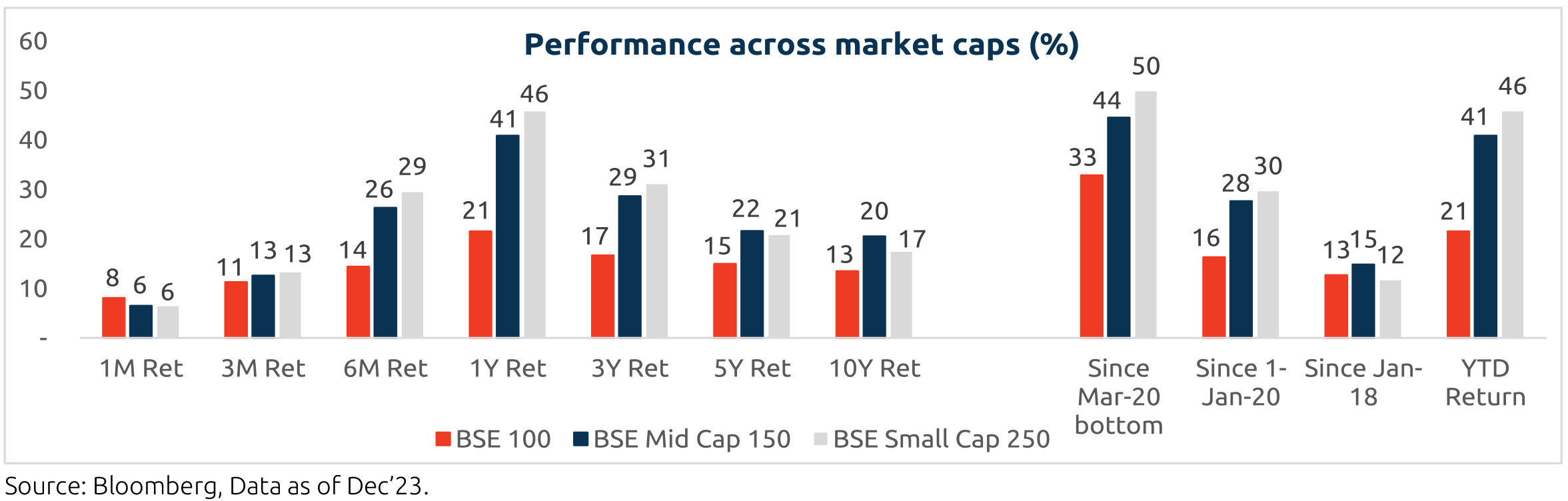
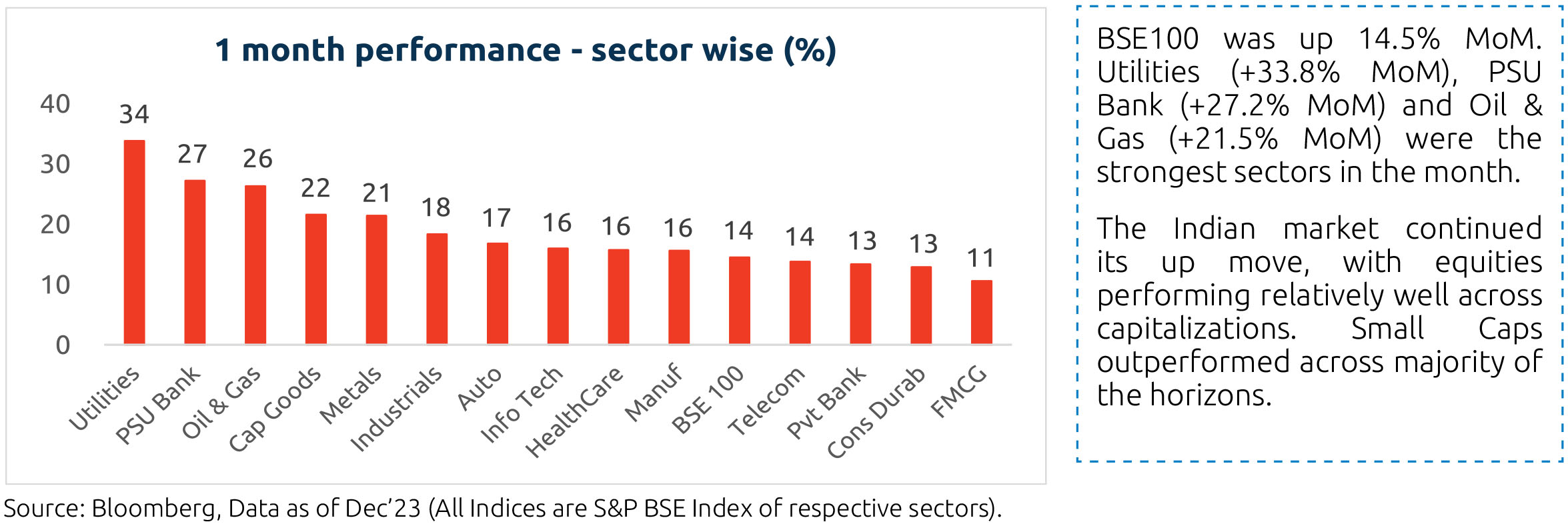
Market Performance
Equity Outlook - Year 2024
- a tale of three probablesAs they say, history doesn't repeat itself but often rhymes. As we approach 2024 having seen high inflation followed by high interest rates globally over the last 2 years, we can look at 3 cycles of the US in the past, which may serve as a blueprint for the way ahead:
Cycle I - The 1994-95 cycle: Soft landing
This was a benign cycle where the Fed tightened preemptively, and the outcome was one of the few truly soft landings in US economic history. The unemployment rate had fallen since 1992, and GDP growth was reasonably healthy, between 2.5% and 4% in 1992-94. At the beginning of 1994, inflation was above 2.5%, and the Fed increased interest rates swiftly from 3% to 6% by March'95. Inflation was controlled, peaking at 3% in June'95, and GDP growth slowed down to 2.25% in Dec'95 with inflation at 2.5%. The improvement in macroeconomic conditions laid the base for an upcycle of more than 4% real GDP growth till 2000. The dollar weakened, with the US Dollar index falling from 97 in Jan'94 to 82 in Jun'95.
Cycle II - The 1973-79 cycle: Inflation strikes back
The US economy performed well during 197-73 with GDP growth crossing 5% in 1972. Due to tightness in oil markets and loose fiscal/monetary policy, inflation galloped to above 12% in 1974. Fed increased rates to 12% in mid-1974 but started cutting aggressively once inflation fell. Inflation bottomed out at the end of 1976 at 5%, with the Fed rate at 4.6%. Subsequently, due to the increase in commodity prices and GDP growth recovery, inflation rebounded, reaching a peak of 15% in 1980. Fed had to raise rates to 19% to get inflation down, causing recessionary conditions from 1980-82. The dollar was weak through this period of 1973-80.
Cycle III - The 1945-50 cycle: Negative real rates for deleveraging the government debt
During the early 1940's due to World War II, the government sought to maintain price stability through the imposition of wage and price controls. After the war, as these controls were dismantled, the price level surged upward. Notably, consumer price inflation averaged 10% from 1946 to 1948. Also, the government debt-GDP had climbed to above 100% by 1946 from 40% before the war. Despite the high inflation, the Fed kept the yield on long-term bonds capped at 2.5% during 1945-1951, hence running high negative real rates. This helped the economy recover to 4% GDP growth in 1948, and government debt to GDP fell swiftly to 75% by 1950.
Our view of how 2024 may shape up in terms of the above cycles:
At this point, the current cycle most likely resembles 1994-95 Cycle, where inflation in the US has come down to 3% from a peak of 9% in Jun'22. Even as the Fed has increased rates to more than 5%, the GDP growth has remained strong, and unemployment is at a multi-decade low. If the Fed continues to keep real rates relatively high, then the US economy should slow down in 2024, with interest rates falling gradually. Given slowing global GDP growth as a headwind and lower interest rates as a tailwind for equity markets, it could be a neutral outcome.
The next likely outcome is that the Fed is more aggressive in cutting rates as the government debt to GDP is as high as in 1945-50 Cycle - if this occurs, equities could get a boost as this could help both the economy and valuations (through better liquidity). The downside risk is a resurgence in inflation like the 1973-79 Cycle - we believe the probability of this is low. Finally, there is a tail risk of the monetary tightening causing a big credit event or deep recession - as the tightening cycle is mature this risk has reduced over the last year. Overall, the chances of emerging markets outperforming developed markets are high in 2024 as interest rates in the latter start coming down.
Things are clearer on the domestic side. Noticeably, India remains a bright spot for global growth with long-term structural positives - strong demographics, political stability, stable macroeconomic indicators, etc. The reforms in the economy a few years back are now paying off through robust tax collections, improvement in the quality of government expenditure with a focus on infrastructure, boost to manufacturing through the PLI scheme and other measures, etc. Most other large emerging countries like China, Brazil, Taiwan, Saudi Arabia, etc. have issues around growth or geopolitics and this should help India garner a big share of global capital flows into emerging markets.
Indian markets have done well in 2023 in absolute terms and relative to the emerging markets index. The broader markets have significantly outperformed large cap indices. While the macro context looks supportive of equities it would be unrealistic to expect such high returns to continue in the broader market. However, for the patient investor who can look at equities from a long-term perspective the small and midcap space still deserves a healthy allocation in our view.
Source: Bloomberg
Sway : A Year In Macro And Bonds
Another year is gone and the mandatory pen to paper needs putting to reflect and forecast. But if we make it sound like this is a chore, it is not. While threatening to be long-drawn, these year-end pieces nevertheless are good vehicles to recap what went by and to provide some flavor of what we expect in the year ahead. A learning with age, however, is to present all views with liberal doses of humility. This is especially given the context of this very strange post pandemic global macro-economic cycle.
Before we get down to the brass tacks, a little elaboration on the title of this piece: The word 'sway' has varied connotations and applications. These range from gently rocking with quiet abandon to almost staggering but not quite falling. There's also a color of dominance in a different interpretation: to hold sway over something. Used yet another way, the word connotes getting carried away.
The Sway Of US Fiscal Policy
Most of the current year has been spent by markets in trying to find the top of the rate hike cycle for the Western world. It wasn't supposed to be this difficult, what with central banks already having put in significant tightening over 2022 itself. 2023 was supposed to be the year for bonds as animal spirits fatigued against the onslaught of rapid monetary tightening, greed turned to fear, and investors rushed to the safety of fixed income. Indeed a trailer for this movie did play for some weeks early in the year, triggered by crises at some banks in US and Europe. However, this proved to be a false start and we rapidly went back to the narrative of sticky inflation and continued rate tightening.
A lot of the growth narrative for the year has originated from the resilience of the US economy. This in turn has been driven by an extra-ordinarily large fiscal tap that was opened up during the Covid period, but which still is far above its pre-pandemic run rate even as growth has been above trend and doesn't justify this. That said, inflation even outside of the tradeable goods sector has fallen in the US as well. More than growth slowdown this reflects a surprising and welcome response from the supply side as the labor pool has expanded and productivity has risen. However, for the Fed to be confident that progress towards its 2% inflation target is sustainable, it now needs to see a period of below trend growth. Data and commentary since October seem to suggest that this indeed may be the case. As the year turns, market hopes of a soft landing have revived with gusto and the expectation is of significant rate cuts over 2024.
It is much clearer in the Eurozone that growth is beginning to sway under pressure from an aggressive monetary tightening program. As the year concludes, this region is already in the midst of sub-par growth with an imminent threat of it sliding into recession. Further east, China's growth dynamics are clearly reflecting the drag from high leverage, weak consumer confidence, and a struggling real estate sector; interspersed with growth stabilizing fiscal and monetary measures. On net however, most analysts don't expect much of a rebound even over the coming year. This is partly owing to the absence of any signal that China is planning any large scale stimuli to significantly boost short term growth.
Swaying Into Landing
A central question for markets next year will be what kind of landing will the developed market (DM) world see? Going into the new year investors are generally poised towards expecting a soft landing: a period of below trend growth with inflation falling back towards target allowing for significant monetary policy easing. At the time of writing, market pricing is for the Fed to deliver approximately 125 - 150 bps of rate cuts over 2024 with the first one latest by May. Expectations with respect to the ECB are also broadly similar. This is why the festival season is upon both the equity and the bond markets. This expectation is driven by economic data nudging in the right direction over the last couple of months.
That said the rate cycle has been aggressive over a short span of time, and the resilience imparted by earlier fiscal transfers may be beginning to fade. The lagged impact of the tightening may yet manifest in its full force in the year ahead, especially as some part of low cost liabilities locked in at lower rates start to come due for refinancing. Also, DM central banks have received a reasonable scare with the inflation episode witnessed over the past couple of years. This may potentially weigh on the extent of aggression that they display when easing monetary policy in response to fall in growth. Thus there is possibility of a scenario where financial conditions actually net tighten even as nominal interest rates are being cut, if the pace of such easing doesn't keep up with the pace of underlying economic growth deterioration. This will open up prospects of a so called 'hard landing' where the behavior of economic agents becomes self-iterative and the downward momentum overshoots. Quality bonds will do well in this scenario but growth assets will struggle.
A third pathway could be that the current phase of softer inflation prints turns out to be yet another false dawn thereby triggering another round of response from DM central banks. This would mean even tighter policy with the risk of higher lagged impacts down the line. In this scenario, both bonds and growth assets will likely lose performance in the first instance.
We have discussed alternate paths above because this cycle has been different and complex thus far and since asset markets seem positioned for just one outcome. Granted that probability of a soft landing is high, especially since the Fed's pivot in its December policy. However, we would assign non trivial weights to the other two scenarios discussed here as well, especially to the second one: momentum overshoot on the downside + controlled aggression in monetary easing = risk of hard landing. Asset allocation considerations may have to be more alive to these lower probability eventualities than they currently are, in our view. We will discuss this later in this note.
India: Swaying To Its Own Macros
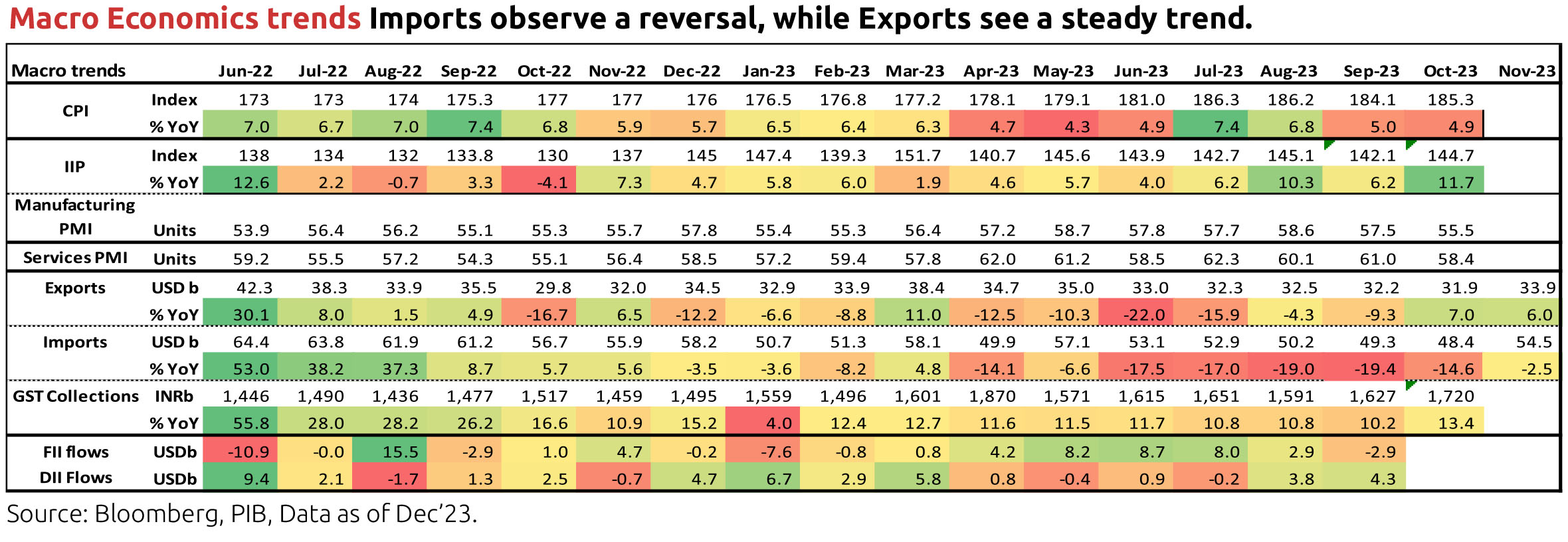
India continues to enjoy very strong macro-economic dynamics. Growth has surprised to the upside. After a slow start, tax revenue growth has made a sharp recovery thereby removing any potential risk of fiscal slippage in the face of higher spending pressures from subsidies and welfare schemes. Headline inflation has been volatile but purely on account of weather driven volatility in food prices while various core measures on inflation remain very well behaved. Finally, and quite notably, India's current account dynamics have turned more robust with a shift up seen in the monthly services trade surplus over the past few quarters.
A lot of this resilience is owed to macro-policies pursued over the past few years including a responsible expansion of fiscal deficit as pandemic response, calibrated monetary stimuli, and proactive subsequent reversal. Besides this, we have also been well poised to capture global shifts. Acceleration in service offshoring over the past few years has led to a fresh leg up in the expansion of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India. As noted above, this has imparted new resilience to our current account dynamics. Also important to our current macro-economic narrative is the fact that the cycle of balance sheet stress has run its course thereby whetting the appetite for a new widespread credit cycle. This has leaned towards retail expansion over the past few years. The conducive terms of lending has helped fuel a significant consumption boom, even though some benefit of doubt to how this growth is looked at needs to be made for the period lost to Covid. However, as with any cycle, there is a risk of overextension in at least some part of retail lending. Consistent with this thought, RBI has acted proactively to enhance risk weights on certain aspects of this piece. Corporate balance sheets are also generally more resilient now and a lot of recent upturn in capex thus far has been financed largely via internal accruals even as lenders remain hopeful that continued capex expansion will soon lead to loan disbursals to corporates.
While India's structural story remains strong, we do expect a cyclical slowdown in growth over the year ahead. This will likely be on account of leveraged consumption slowing, the blistering pace of government capex spending normalizing, as well as a possible drag from the external sector as global growth slows further. A counter-balance may be provided if private capex continues to broad-base as seems to be the commentary in many quarters. However, given a likely rise in global economic uncertainty some deferment in this broad-basing may entirely be par for the course.
Don't Get Swayed
Most of the last one and a half years for fixed income investors has been about managing volatility thrown up by central banks moving from more than usually loose monetary policy to more than usually tight policy over a short period of time. This observation is more in context of DMs where, especially with benefit of hindsight, it can be argued that policy easing went overboard and hence the journey back had to be daunting. What is noteworthy also is that this whole journey was made even as the underlying environment for risk taking remained largely benign, or at worst recovered very quickly. Even more, as the narrative of soft landing in the Western world has taken firmer roots, the appetite for risk has become even more magnified. It is to be noted that the reference here is to pro-cyclical risk taking and not for duration risk. It is also to be noted that this last reference, and the observations below, pertain to our domestic market.
Over the monetary tightening cycle, the natural inclination for investors has been to minimize duration risk while seeking higher carry or accrual income. Given the pressure faced by lenders on the liability side, investors have got lucrative deposit rates. Additionally, and especially since the tax change for debt mutual funds, a lot of investors have been adding allocations to private credit funds. However, if our view of cycle peak on both interest rates and economic growth is correct, then it is time for a review with the following pointers in mind:
Swaying To The New Year
Another year with material weight for markets and the world is ending. For a long-suffering bond market, we look forward to a confluence of three bullish factors from India's perspective: 1> Cycle peak on rates 2> Benign current account dynamics arguing for stable long-term rates 3> Greater international interest for our bonds with the near-term trigger being the index inclusion.
DM central banks have taken policy rates to levels much higher than what may be assessed as long term neutral in those geographies. Thus the scope for cuts is that much more. India's case is different where deft macro-management has allowed us to get away with a more modest rate hike cycle, hence also allowing for more modest cuts. However, these dynamics are already reflected in the shape of respective yield curves. DM yield curves are deeply inverted and ours is still decently positively sloping at the top of the cycle, thereby allowing for scope for a decent move lower in market yields even with relatively modest easing expectations in policy rates. We expect 50 -75 bps rate cuts from RBI, most likely over the second half of 2024. While not our base case, should there be a hard landing in the West, then these cuts could be deeper.
And that is pretty much the wrap. Here's wishing that the new year brings enough joy so that when you close your eyes and reminisce, you sway in the best way possible: with a quiet smile that if someone notices makes them smile as well, to the gentle rhythm of a music which is home to you.
Wishing You A Very Happy New Year.
Source: Bandhan MF Research
Another year is gone and the mandatory pen to paper needs putting to reflect and forecast. But if we make it sound like this is a chore, it is not. While threatening to be long-drawn, these year-end pieces nevertheless are good vehicles to recap what went by and to provide some flavor of what we expect in the year ahead. A learning with age, however, is to present all views with liberal doses of humility. This is especially given the context of this very strange post pandemic global macro-economic cycle.
Before we get down to the brass tacks, a little elaboration on the title of this piece: The word 'sway' has varied connotations and applications. These range from gently rocking with quiet abandon to almost staggering but not quite falling. There's also a color of dominance in a different interpretation: to hold sway over something. Used yet another way, the word connotes getting carried away.
The Sway Of US Fiscal Policy
Most of the current year has been spent by markets in trying to find the top of the rate hike cycle for the Western world. It wasn't supposed to be this difficult, what with central banks already having put in significant tightening over 2022 itself. 2023 was supposed to be the year for bonds as animal spirits fatigued against the onslaught of rapid monetary tightening, greed turned to fear, and investors rushed to the safety of fixed income. Indeed a trailer for this movie did play for some weeks early in the year, triggered by crises at some banks in US and Europe. However, this proved to be a false start and we rapidly went back to the narrative of sticky inflation and continued rate tightening.
A lot of the growth narrative for the year has originated from the resilience of the US economy. This in turn has been driven by an extra-ordinarily large fiscal tap that was opened up during the Covid period, but which still is far above its pre-pandemic run rate even as growth has been above trend and doesn't justify this. That said, inflation even outside of the tradeable goods sector has fallen in the US as well. More than growth slowdown this reflects a surprising and welcome response from the supply side as the labor pool has expanded and productivity has risen. However, for the Fed to be confident that progress towards its 2% inflation target is sustainable, it now needs to see a period of below trend growth. Data and commentary since October seem to suggest that this indeed may be the case. As the year turns, market hopes of a soft landing have revived with gusto and the expectation is of significant rate cuts over 2024.
It is much clearer in the Eurozone that growth is beginning to sway under pressure from an aggressive monetary tightening program. As the year concludes, this region is already in the midst of sub-par growth with an imminent threat of it sliding into recession. Further east, China's growth dynamics are clearly reflecting the drag from high leverage, weak consumer confidence, and a struggling real estate sector; interspersed with growth stabilizing fiscal and monetary measures. On net however, most analysts don't expect much of a rebound even over the coming year. This is partly owing to the absence of any signal that China is planning any large scale stimuli to significantly boost short term growth.
Swaying Into Landing
A central question for markets next year will be what kind of landing will the developed market (DM) world see? Going into the new year investors are generally poised towards expecting a soft landing: a period of below trend growth with inflation falling back towards target allowing for significant monetary policy easing. At the time of writing, market pricing is for the Fed to deliver approximately 125 - 150 bps of rate cuts over 2024 with the first one latest by May. Expectations with respect to the ECB are also broadly similar. This is why the festival season is upon both the equity and the bond markets. This expectation is driven by economic data nudging in the right direction over the last couple of months.
That said the rate cycle has been aggressive over a short span of time, and the resilience imparted by earlier fiscal transfers may be beginning to fade. The lagged impact of the tightening may yet manifest in its full force in the year ahead, especially as some part of low cost liabilities locked in at lower rates start to come due for refinancing. Also, DM central banks have received a reasonable scare with the inflation episode witnessed over the past couple of years. This may potentially weigh on the extent of aggression that they display when easing monetary policy in response to fall in growth. Thus there is possibility of a scenario where financial conditions actually net tighten even as nominal interest rates are being cut, if the pace of such easing doesn't keep up with the pace of underlying economic growth deterioration. This will open up prospects of a so called 'hard landing' where the behavior of economic agents becomes self-iterative and the downward momentum overshoots. Quality bonds will do well in this scenario but growth assets will struggle.
A third pathway could be that the current phase of softer inflation prints turns out to be yet another false dawn thereby triggering another round of response from DM central banks. This would mean even tighter policy with the risk of higher lagged impacts down the line. In this scenario, both bonds and growth assets will likely lose performance in the first instance.
We have discussed alternate paths above because this cycle has been different and complex thus far and since asset markets seem positioned for just one outcome. Granted that probability of a soft landing is high, especially since the Fed's pivot in its December policy. However, we would assign non trivial weights to the other two scenarios discussed here as well, especially to the second one: momentum overshoot on the downside + controlled aggression in monetary easing = risk of hard landing. Asset allocation considerations may have to be more alive to these lower probability eventualities than they currently are, in our view. We will discuss this later in this note.
India: Swaying To Its Own Macros
India continues to enjoy very strong macro-economic dynamics. Growth has surprised to the upside. After a slow start, tax revenue growth has made a sharp recovery thereby removing any potential risk of fiscal slippage in the face of higher spending pressures from subsidies and welfare schemes. Headline inflation has been volatile but purely on account of weather driven volatility in food prices while various core measures on inflation remain very well behaved. Finally, and quite notably, India's current account dynamics have turned more robust with a shift up seen in the monthly services trade surplus over the past few quarters.
A lot of this resilience is owed to macro-policies pursued over the past few years including a responsible expansion of fiscal deficit as pandemic response, calibrated monetary stimuli, and proactive subsequent reversal. Besides this, we have also been well poised to capture global shifts. Acceleration in service offshoring over the past few years has led to a fresh leg up in the expansion of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India. As noted above, this has imparted new resilience to our current account dynamics. Also important to our current macro-economic narrative is the fact that the cycle of balance sheet stress has run its course thereby whetting the appetite for a new widespread credit cycle. This has leaned towards retail expansion over the past few years. The conducive terms of lending has helped fuel a significant consumption boom, even though some benefit of doubt to how this growth is looked at needs to be made for the period lost to Covid. However, as with any cycle, there is a risk of overextension in at least some part of retail lending. Consistent with this thought, RBI has acted proactively to enhance risk weights on certain aspects of this piece. Corporate balance sheets are also generally more resilient now and a lot of recent upturn in capex thus far has been financed largely via internal accruals even as lenders remain hopeful that continued capex expansion will soon lead to loan disbursals to corporates.
While India's structural story remains strong, we do expect a cyclical slowdown in growth over the year ahead. This will likely be on account of leveraged consumption slowing, the blistering pace of government capex spending normalizing, as well as a possible drag from the external sector as global growth slows further. A counter-balance may be provided if private capex continues to broad-base as seems to be the commentary in many quarters. However, given a likely rise in global economic uncertainty some deferment in this broad-basing may entirely be par for the course.
Don't Get Swayed
Most of the last one and a half years for fixed income investors has been about managing volatility thrown up by central banks moving from more than usually loose monetary policy to more than usually tight policy over a short period of time. This observation is more in context of DMs where, especially with benefit of hindsight, it can be argued that policy easing went overboard and hence the journey back had to be daunting. What is noteworthy also is that this whole journey was made even as the underlying environment for risk taking remained largely benign, or at worst recovered very quickly. Even more, as the narrative of soft landing in the Western world has taken firmer roots, the appetite for risk has become even more magnified. It is to be noted that the reference here is to pro-cyclical risk taking and not for duration risk. It is also to be noted that this last reference, and the observations below, pertain to our domestic market.
Over the monetary tightening cycle, the natural inclination for investors has been to minimize duration risk while seeking higher carry or accrual income. Given the pressure faced by lenders on the liability side, investors have got lucrative deposit rates. Additionally, and especially since the tax change for debt mutual funds, a lot of investors have been adding allocations to private credit funds. However, if our view of cycle peak on both interest rates and economic growth is correct, then it is time for a review with the following pointers in mind:
- As discussed above, the last 18 months of interest rate volatility has led to active avoidance of duration risk in favor of shorter duration, higher carry assets. However, we think it's time to flip thinking from avoiding duration risk to actively thinking about plugging reinvestment risks from investments maturing over the next year or so. Given that a substantial part of allocations made over the past couple of years will be inflexible (locked away either in deposits or in mutual funds under the old tax regime), one will then need to make new investments of sufficiently long maturities in order to be able to lift average maturity on the entire portfolio and thereby partly counter reinvestment risks arising from future maturing investments.
- In any robust asset allocation one has to have both pro-cyclical and counter-cyclical assets, and hence there is need for quality fixed income to fulfill the latter. By definition yield on credit will always be better than yield on quality. However, the relative value between the two is assessed by the credit spread and how it stands in relation to longer term averages. It can be argued that like to like, credit spreads are at or close to cycle lows (there has been some recent expansion). Hence this is the time when relative value in quality fixed income is better and investors should use this period to build quality in their asset allocation. We expect spreads to widen over the next few quarters, thereby providing investors with a better opportunity to add to credit later. Conversely, if the focus remains on credit even today when the relative value has shifted towards quality fixed income, then one has to wonder when at all the counter-cyclical quality fixed income allocation will get built?
- Especially since the debt MF tax change, the allocation to pro-cyclical assets including private credit has moved up. Thus far the cycle narrative has also supported these allocations. It is reasonable to assume basis evidence over multiple previous cycles, that many investors' risk appetites may be stretched by now even as the robust price performance so far is still keeping the true appetite hidden. Also learned from earlier cycles is the tendency to turn a half-decent narrative into an investment thesis during the full-blown phase of risk taking. An example here, for illustration: the move to higher credit risk is being 'justified' by the narrative of cleaner balance sheets. This, of course, is true for the aggregate. What is also true, however, is that almost by definition the spreads on offer for balance sheets that have cleaned up have compressed. These aren't necessarily the credits being bought since yield pick up here has diminished. Instead the broad-brush narrative of clean balance sheets may be leading allocations into areas where this narrative may not be entirely relevant (and hence one gets higher risk spread). As another example, expected returns on many private credit allocations seem to be closer to what equities are expected to deliver over medium horizons. Unless a large arbitrage has sprung up in markets, again almost by definition this means that the risk profile of such investments is also closer to equities than it is to traditional fixed income. And yet, allocations here are being carved out from what was earlier traditional fixed income allocation prior to the tax change.
- Most asset allocation today is basis the dominant narrative of a soft landing in the Western world. However, as discussed above, there are low but nevertheless non trivial probabilities of a harder landing there. While ramifications to India may still be limited, the relative skew of performance from various asset classes (pro-cyclical and counter-cyclical) may nevertheless be different depending upon what kind of a landing we see for the West. Combining this with the fact that relative value in quality fixed income has improved, and adding the observation that most investors thus far have been aggressively procyclical in their behavior, we think there is a strong case now to build one's quality fixed income book.
Swaying To The New Year
Another year with material weight for markets and the world is ending. For a long-suffering bond market, we look forward to a confluence of three bullish factors from India's perspective: 1> Cycle peak on rates 2> Benign current account dynamics arguing for stable long-term rates 3> Greater international interest for our bonds with the near-term trigger being the index inclusion.
DM central banks have taken policy rates to levels much higher than what may be assessed as long term neutral in those geographies. Thus the scope for cuts is that much more. India's case is different where deft macro-management has allowed us to get away with a more modest rate hike cycle, hence also allowing for more modest cuts. However, these dynamics are already reflected in the shape of respective yield curves. DM yield curves are deeply inverted and ours is still decently positively sloping at the top of the cycle, thereby allowing for scope for a decent move lower in market yields even with relatively modest easing expectations in policy rates. We expect 50 -75 bps rate cuts from RBI, most likely over the second half of 2024. While not our base case, should there be a hard landing in the West, then these cuts could be deeper.
And that is pretty much the wrap. Here's wishing that the new year brings enough joy so that when you close your eyes and reminisce, you sway in the best way possible: with a quiet smile that if someone notices makes them smile as well, to the gentle rhythm of a music which is home to you.
Wishing You A Very Happy New Year.
Source: Bandhan MF Research





